People who have diabetes may suffer from peripheral nerve damage if their blood sugar is not well controlled, especially those who have had the disease for a long time. Half of the diabetic patients who have had the disease for more than 10 years will develop peripheral neuropathy, but the mechanism of disease formation is not clear now, so the treatment should also start from many aspects.
A. Diabetes can cause peripheral neuropathy
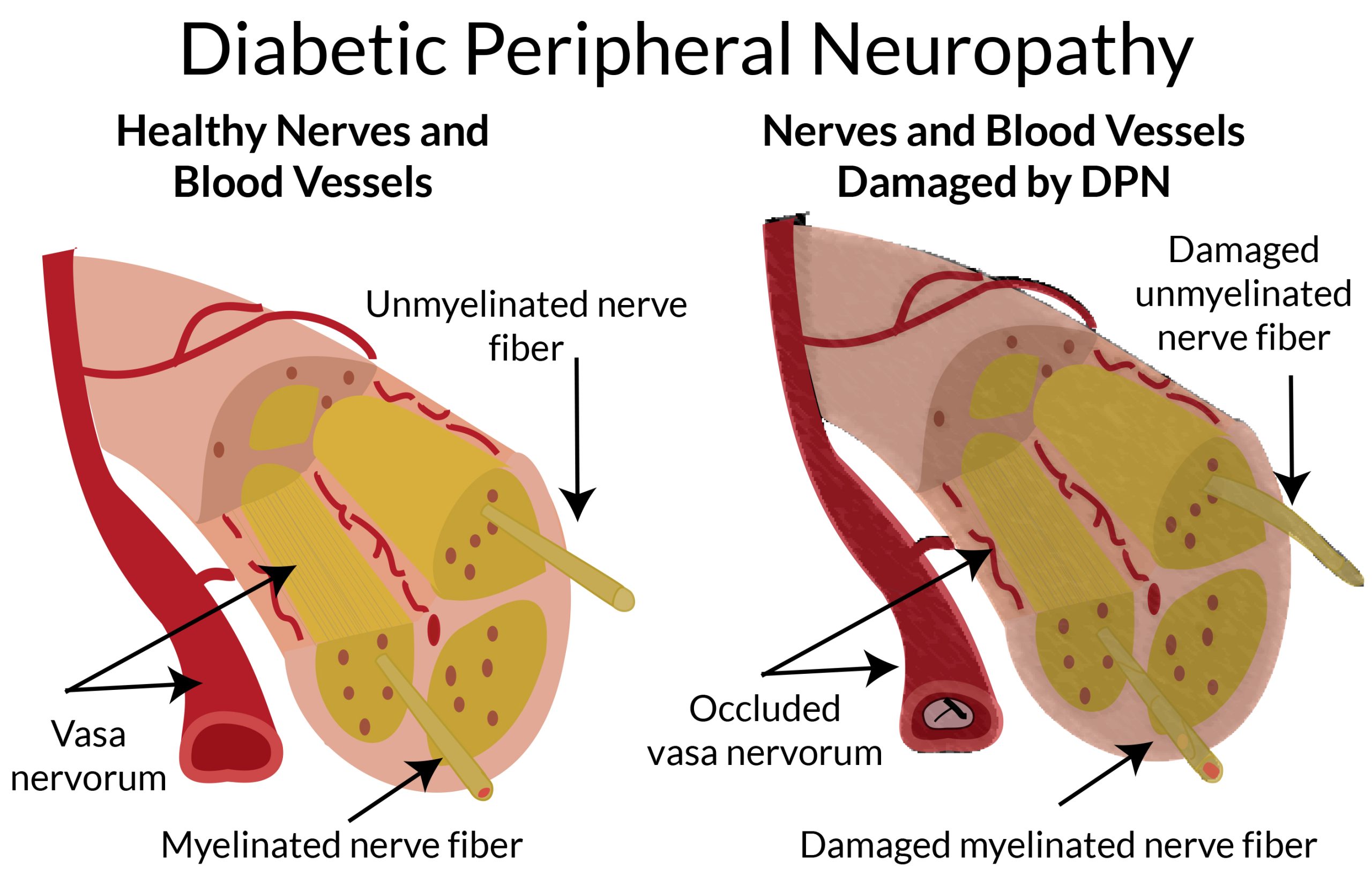
Now people have not understood the exact mechanism of diabetes caused by peripheral neuropathy, but one thing is certain, is related to long-term severe hyperglycemia. This leads to a variety of reactions such as microangiopathy, DNA damage, oxidative stress damage, neuroinflammation, and cellular dystrophy, ultimately leading to irreversible damage to nerve cells.
Typical symptoms of peripheral neuropathy are multiple sensory abnormalities such as burning, pins and needles, ankylosis, numbness, and pain in the distal extremities. It may also involve multiple systems such as cardiovascular, digestive, and genitourinary, resulting in a variety of symptoms such as rapid or slow heart rate, abnormal blood pressure regulation, poor digestion, abnormal urination, and sexual dysfunction.
However, there is no specific diagnosis for this disease. Diabetic patients with the above symptoms may be considered to have diabetic peripheral neuropathy after excluding the effects of other factors such as vascular inflammation, spinal disease, renal insufficiency, thyroid disease, infectious disease, and adverse drug reactions.
Second, control of blood sugar is the key to treatment
Among the possible mechanisms of diabetic peripheral neuropathy, the main one is “sorbitol accumulation hypothesis”. There are two main pathways for the normal metabolism of blood sugar (glucose) in human body, one is aerobic metabolism, which will eventually produce water and carbon dioxide; the other is anaerobic metabolism, which produces lactic acid.
However, when blood glucose is too high, the main metabolic pathway is unable to utilize all of the glucose, which leads to an increase in the bypass metabolism of glucose, causing it to produce sorbitol in the presence of aldose reductase. A large amount of sorbitol accumulation can cause peripheral nerve damage.
Therefore, high blood sugar is the direct cause of the disease, and the key to treatment is to control blood sugar. Generally speaking, controlling glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) within 7% can better prevent peripheral neuropathy.
Third, drug treatment should start from several aspects
The mechanism of diabetic peripheral neuropathy is not exact, and there may be several risk factors, so the drug treatment should also start from many aspects.
1、Improve metabolic disorders: you can use epalrestat, which is an aldose reductase inhibitor that can prevent glucose from being bypassed for metabolism and reduce the production and accumulation of sorbitol.
2, against oxidative stress: you can use lipoic acid, which is a B vitamin, has a strong antioxidant effect, can reduce lipid oxidation of neural tissue, can inhibit protein glycosylation, and also has the effect of inhibiting aldose reductase.
3、Improve microcirculation: you can use pancreatic kininogenase, which can dilate blood vessels, improve microcirculatory disorders, and increase the nutrition and oxygen supply to nerve tissues.
4、Promote nerve repair: Methylcobalamin can be used to promote nucleic acid metabolism and protein synthesis of nerve cells, and promote the transport function and regeneration of axons.
5, relieve pain symptoms: the main symptom of peripheral neuropathy is pain, which can seriously affect the quality of life and requires pain relief treatment. Antidepressants, anti-neuralgia drugs, central analgesic drugs, can be used for pain relief treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy, specific drug selection, need to be under the guidance of doctors.
To sum up, diabetic patients with poor long-term blood sugar control are prone to peripheral neuropathy. Hyperglycemia is the main cause of the disease, and blood sugar control is the key to treatment. However, the mechanism of the disease is not clear now, and drug treatment needs to start from many aspects, and the selection and use of specific drugs need to be carried out under the guidance of a doctor.